

Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition which principally affects the face, and causes skin redness.
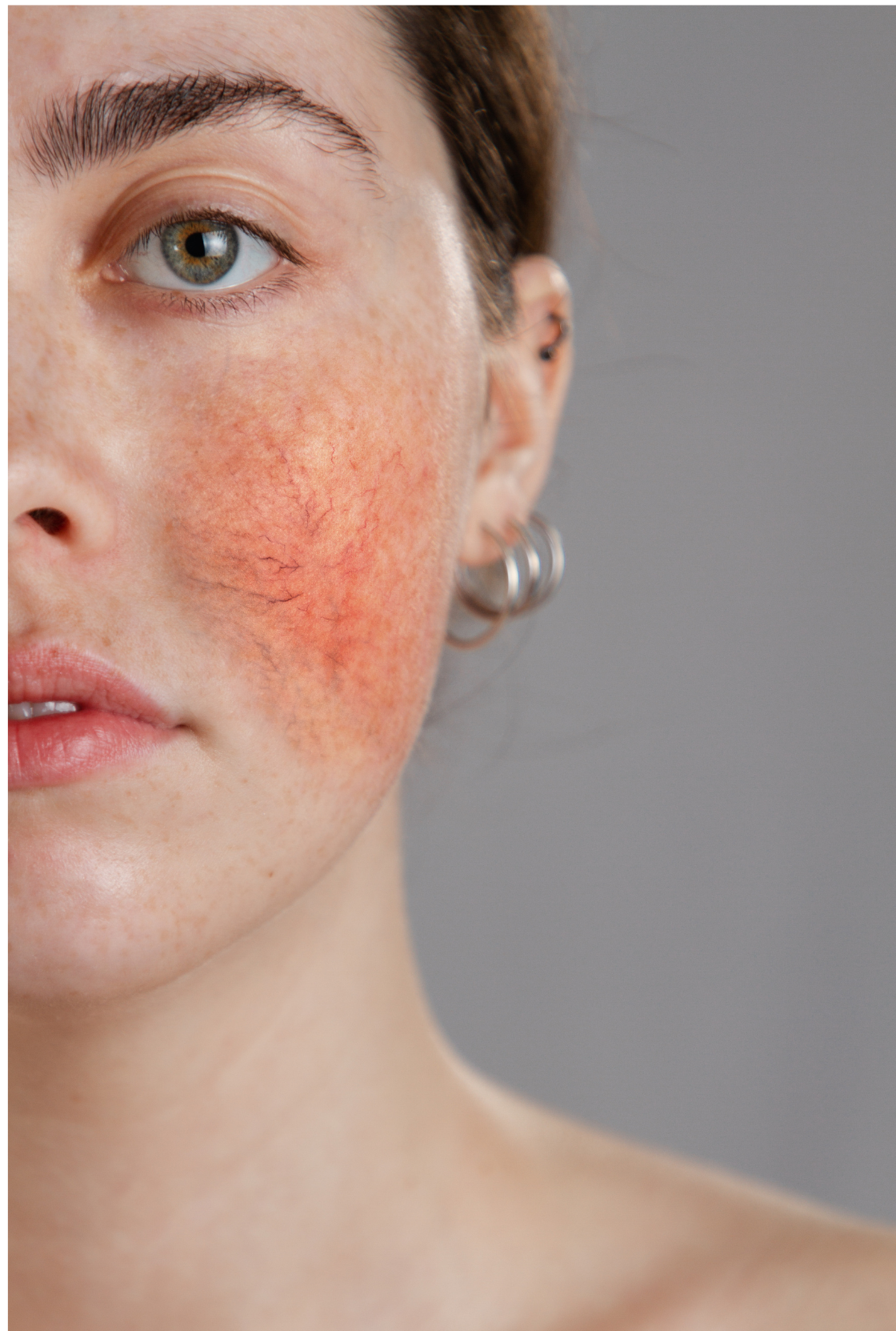

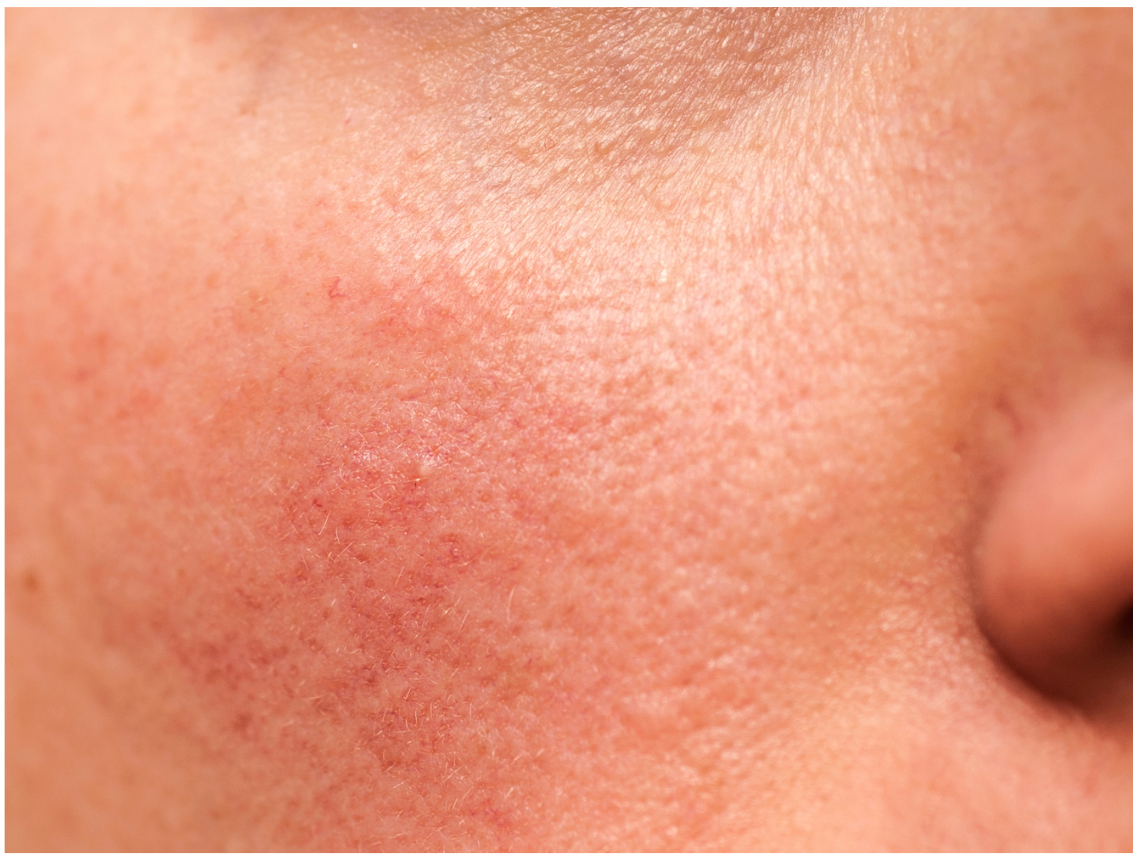
Rosacea: What Is It?
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that mainly affects the face. It often causes persistent redness, visible tiny blood vessels, and episodes of flushing. Symptoms can flare up and settle down over time, and some people also experience burning, stinging, swelling, or spot-like breakouts.
While the exact cause isn’t fully understood, rosacea is known to be influenced by a range of common triggers.
Types of Rosacea
Rosacea is usually grouped into four recognised subtypes:
Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR)
- Flushing and ongoing redness
- Visible small blood vessels
- Sensitive, reactive skin
Papulopustular Rosacea
- Redness with spot-like bumps (can look similar to acne)
- Flare-ups may come and go
Phymatous Rosacea
- Thickened skin with an uneven, bumpy texture
- Most commonly affects the nose (rhinophyma)
- Tends to develop gradually and may worsen without treatment
Ocular Rosacea
- Affects the eyes and eyelids
- Red, irritated, watery eyes and swollen lids
- Symptoms can worsen with environmental exposure
What Triggers Rosacea?
Rosacea often starts with flushing, and can progress to include redness, sensitivity, visible veins, and sometimes bumps. Triggers vary from person to person, but common ones include:
- Environmental factors: sun exposure, wind, extreme temperatures, and rapid temperature changes
- Dietary triggers: spicy foods, hot drinks, and alcohol
- Stress: emotional stress and anxiety can worsen flare-ups
- Skincare products: formulas with alcohol, fragrance, or harsh actives may irritate and trigger symptoms
- Medications: some medicines (including certain blood pressure drugs and topical steroids) may aggravate rosacea. Speak to your GP if you suspect a link
Treatments Include:
- Peel
- Vein Wave
- Sylfirm X
- Peptide/Exosome
- Microtox
- Growth Factor
- Light Therapy

